Cutting the costs: strategies for more affordable CAR-T cell manufacturing
Major cost drivers in CAR-T cell therapy
The cost of CAR-T therapy is influenced by several interconnected factors. First, the reliance on personalized, autologous cells requires individualized manufacturing for every patient. This includes leukapheresis, transport to centralized facilities, viral vector transduction, and extended cell expansion protocols. Secondly, infrastructure requirements, such as GMP-compliant cleanrooms and cold-chain logistics, add additional layers of expense. Finally, quality control (QC) and regulatory compliance demand skilled staff and time-consuming procedures. Altogether, this process can stretch over weeks and cost hundreds of thousands of dollars per dose1.
Innovations in upstream and downstream processing: GoFast™ workflow in point-of-care manufacturing
One way to reduce costs is by reducing the manufacturing timeline. The GoFastTM workflow, for example, is a rapid CAR-T manufacturing approach that minimizes in vitro expansion, reduces workflow complexity and instrumentation, and enables cell production in under 72 hours through a simplified, GMP-ready, three-step process. Strategies include also non-viral transposons and optimized electroporation, to deliver functional CAR-T cells in just days instead of weeks1. These fast-track approaches are not only faster and more affordable but have also been reported to potentially yield a more desirable cell phenotype, favoring less-differentiated, memory-like T cells with higher potency.
In the VELCART trial, CAR-T cells were manufactured on-site, achieving a 15-fold expansion and a vein-to-vein time of just 9 days. This decentralized, streamlined workflow enabled the use of fresh cells, which was associated with reduced toxicity, lower logistical complexity, and median treatment costs under $50,000—well below global benchmarks2. Other emerging approaches have explored similarly rapid manufacturing timelines; for instance, a recent trial reported the feasibility of a 3-day CAR-T production process, suggesting potential benefits in preserving T-cell quality and accelerating treatment delivery3.
Traditional CAR-T manufacturing takes 2–3 weeks, often delaying treatment for critically ill patients. GoFast™ reduces this timeline to under 72 hours, enabling faster delivery of life-saving therapy when every moment counts.
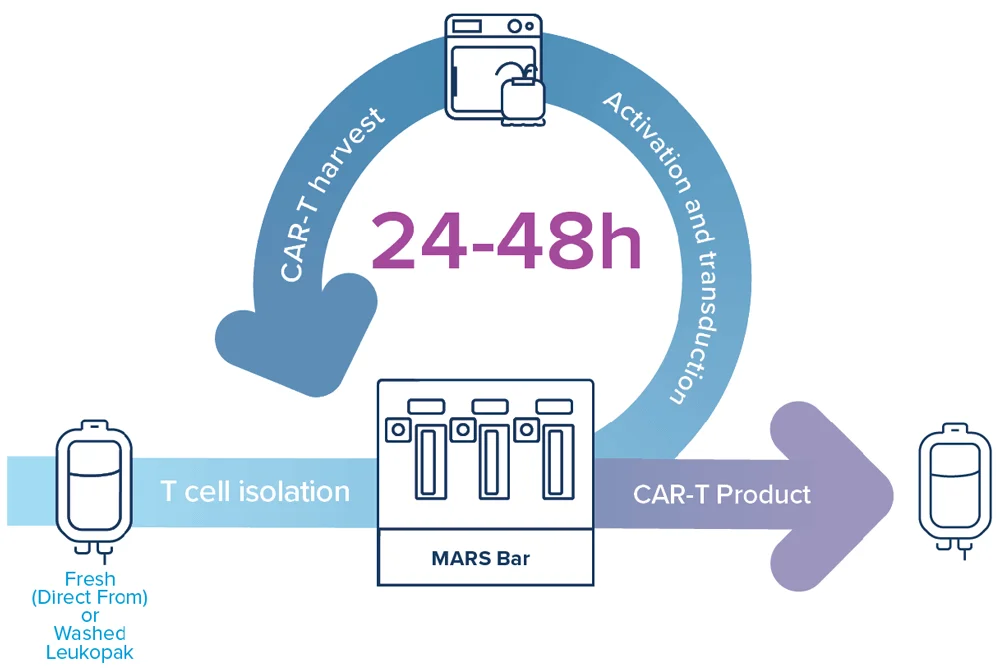
Role of automation and closed systems
Automation and closed-system manufacturing are foundational to cost-effective production. Platforms like MARS® Bar and MARS® Atlas consolidate several manufacture processes into a simple, automated workflow. These systems aim at reducing the need for extensive labor, mitigating contamination risk, and supporting reproducible GMP-compliant workflows across distributed sites. Closed systems also enable decentralized manufacturing, eliminating the need for cryopreservation and complex transport logistics, two of the most significant cost drivers in traditional models1,2.
Standardization and platform-based approaches
Standardization is an important factor on the path to scaling affordable cell therapy, and platform-based manufacturing reduces variation and improves process control. Harmonized protocols and pre-configured systems make it easier to train staff, replicate success across sites, and meet regulatory expectations. Importantly, standardization also supports faster adaptation to new vectors, protocols, and therapeutic targets, reducing the overall cost and risk of innovation.
By adopting unified systems and validated workflows, manufacturers can transition toward a more platform-based model, similarly to how antibody therapeutics have scaled over time. Point-of-care centers implementing such platforms can replicate high-quality outcomes even outside major industry hubs.
Conclusion
CAR-T therapy is no longer a scientific novelty, but is quickly becoming a clinical necessity. But for this therapeutic approach to reach its full potential, costs must be addressed head-on. Through the adoption of closed-system automation, decentralized production, shortened expansion protocols, and standardized platforms, manufacturers can significantly reduce expenses while maintaining product quality. At Applied Cells, we believe in a future where every patient, no matter the geography or level of income, can access life-saving cell therapies. Our mission is to enable scalable cell therapy manufacturing, with a vision to help reduce manufacturing COGS below $7,000 with GoFastTM workflow.
Interested in learning more about how we support affordable cell therapy manufacturing? Contact us today.
References
- Abdo L, Batista-Silva LR, Bonamino MH. Cost-effective strategies for CAR-T cell therapy manufacturing. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2025;33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omton.2025.200980
- Palani HK, Arunachalam AK, Kulkarni U, et al. Safety, efficacy and total cost of point-of-care manufactured anti-CD19 CAR-T cell therapy in India: VELCART trial. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2025;33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omton.2025.200977
- Svoboda J, Landsburg DJ, Gerson J, et al. Enhanced CAR T-cell therapy for lymphoma after previous failure. N Engl J Med. 2025;392(18):1824–1835. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2408771

